Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India

The scientific community widely acknowledges global climate change as an undeniable reality, posing a significant threat to the Earth and its inhabitants. However, despite the overwhelming consensus among experts, there are instances where misleading conversations, often disseminated through social media platforms, attempt to cast doubt on the existence of climate change, portraying it as a hoax or scam. Though lacking scientific merit, these misleading narratives contribute to misinformation and confusion surrounding one of the most pressing issues of our time.
Social media posts
A 20-minute video is being shared on social media along with the message, “The World Economic Forum is pushing their climate change agenda, and the media is following suit, but they don’t tell the whole story. There are a lot of questions a studious person should ask about climate change. so we are going to ask them and show how it can be dangerous to prioritise sustainability and climate alarmism.” Many people viewed the message and shared their thoughts on it.
The video script discusses different scenarios and makes them relate to climate change. We checked into the content of the video and summarised those points.
Claims can be identified as follows.
2:36-4:10 minutes – Climate variability and climate change are not the same, and the impact of human activity on climate change is not definitively proven.
4:11-6:15 minutes – The Atlantic multi-decadal oscillation and increased volcanic activity can contribute to climate variability and cooling.
6:16-8:25 minutes – Current climate models do not account for solar variation or future volcanic eruptions, raising questions about their accuracy.
10:26-12:10 minutes – The increased volcanic activity and its historical impact on climate cooling.
12:11-14:55 minutes – Globalists and the media’s urgency in pushing climate change may lack scientific evidence and rely on incomplete data.
So, as a summary, the video script raises concerns about increased volcanic activity and its potential impact on cooling. At the same time, it calls for further research and investigation into the role of volcanic eruptions in shaping global temperatures. The script highlights the limitations of current climate models in accounting for solar variation, future volcanic eruptions, and natural climate variability such as the Atlantic multi-decadal oscillation.
We decided to do a fact-check on this.
Fact Check
Climate Variability and Climate Change
Weather is highly changeable daily, weekly, or even annually. The climate is the sum of weather over time, while Earth’s climate is about how to change the planet’s temperature on average with solar radiation from the sun.
However, climate does not change on a small scale or day-to-day basis. It is all about longer time scales and averages. The greenhouse effect regulates the earth’s temperature to be appropriate for humans and other lives. However, with the excessive use of resources with higher carbon footprints and environmental pollution, humans are loading the atmosphere with more and more greenhouse gases. These gases are scientifically proven to trap solar energy, otherwise emitted to space as outgoing longwave radiation. This is a simple and proven explanation for global warming. Global warming leads to climate change, which is about increasing temperatures and extreme weather events and variables.
Climate variability refers to the deviation of certain aspects of the climate, like temperature and precipitation, from the mean. Volcanic eruptions, natural and occasionally recurring variations in the air and ocean circulation, and other factors contribute to climate variability.
For instance, this graph shows the average daily maximum temperature in July, averaged over 30 years from 1988 through 2017, in Boulder, Colorado, which was 87.7° F (30.9° C). However, in some years, July has been warmer than the average. In other years, the month of July is better than average.
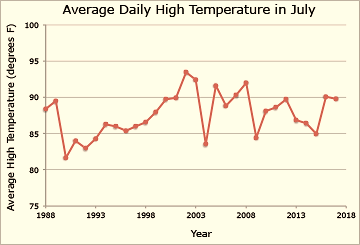
Source – Climate Variability | Center for Science Education (ucar.edu)
The critical fact here is that the average global temperature is a little the same yearly. Also, the previous year could be a little hotter than the present year, which means the present year is a little cooler. However, the long-term trend shows increasing temperatures due to climate change.
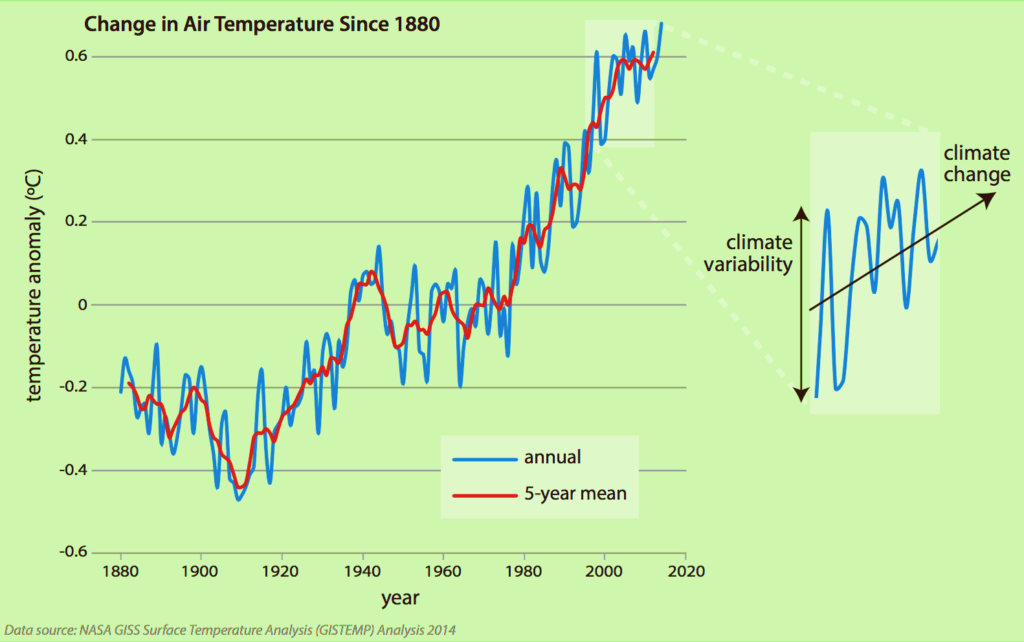
Source – Climate Variability | Center for Science Education (ucar.edu) | What Is Climate Change? | Facts – Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet (nasa.gov)
Various factors, including natural oscillations like the ENSO, cause climate variability. (El Nino Southern Oscillation). AMO is also a climate variability. The presenter is talking about the Atlantic Multi-decadal Oscillation (AMO), recognised as a consistent pattern of long-term natural variability occurring in the North Atlantic Ocean between 60 and 80 years. The average anomalies of sea surface temperatures are typically over 0-80N in the North Atlantic basin, which serves as its foundation.
Is climate change all about a 1° C rise in temperature?
A one-degree rise in temperature may seem insignificant, but the real-world consequences of a one °C rise in temperature are significant and wide-ranging. It’s also important to understand that Earth is not warming evenly and is not predicted to. Generally, middle and high latitudes will warm more than the tropics, and land surface temperatures will rise more than ocean temperatures. Land masses in the United States are predicted to warm significantly faster than the global average over the long run.
Read More – A Degree of Concern: Why Global Temperatures Matter – Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet (nasa.gov)
Volcanic Eruptions and Global Cooling
The discussion claims the potential impact of increased volcanic activity on climate variability and cooling. New research challenges previous estimates regarding the extent of global cooling caused by super-volcanic eruptions, suggesting that the cooling effect may be less severe.
A time of widespread cooling on Earth is referred to as the ‘Little Ice Age’. Although scientists cannot agree on a start and end date, it is generally accepted to have continued into the 19th century. Strong volcanic eruptions can cause a cooling effect that prolongs the Little Ice Age, as can variations in the Arctic ice cover.
There was a slight global shift during the Little Ice Age, but there was an increase in harsh winters in some parts of Europe. A study proposes four violent volcanic eruptions in the tropics between approximately 1250 and 1300, which would have shot massive sulfate particle clouds into the upper atmosphere. Because they reflect solar energy into space, these minuscule aerosol particles are known to cool the planet. But it’s thought that the aerosols from volcanic eruptions typically only cause a brief climate cooling.
Read more – Will there be an Ice Age in another 15 years? – Climate Fact Checks
There are ongoing uncertainties regarding the impact of super-eruptions on global temperatures. Comprehensive comparisons of models and additional laboratory and model studies are needed to understand better the factors determining volcanic aerosol particle sizes. In summary, while super-volcanic eruptions have the potential to influence global temperatures, the exact extent of their cooling effect remains uncertain.
Read More: Exploring Climate Change Skepticism: Why Climate Change Is Not A Scam?
Conclusion
The claims made in the viral social media video are misleading and incomplete. While the discussion in the video attempts to discredit the reality of climate change by citing irrelevant data and presenting incomplete arguments, a comprehensive review of scientific literature and evidence strongly supports the reality of anthropogenic climate change.
As independent fact-checking, it seems the presenters focus on isolated incidents, such as temporary fluctuations in temperature or individual weather events and fail to acknowledge the overwhelming consensus regarding the long-term trends and impacts of climate change.
-With inputs from Nuwandhara Mudalige –