Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
We recently came across viral social media posts highlighting the trees and their functionality as plants producing oxygen were overrated. Hence more importance needs to be given to oceanic plankton, as seen below. As we all know, millions of living species depend on Oxygen for breathing, including humans. Has the oxygen percentage been the same throughout history? What provides the highest percentage of Oxygen to the planet? These are some of the intriguing questions many argue about.
When asked about what kind of plants mostly produce oxygen, most would comment on an abundance of green trees. While most are aware of the importance of trees and their photosynthesis process, the same cannot be said about sea plants, specifically sea plankton.
Social Media Posts
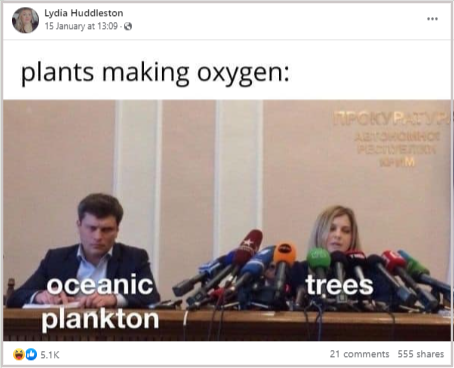
Below are how users commented
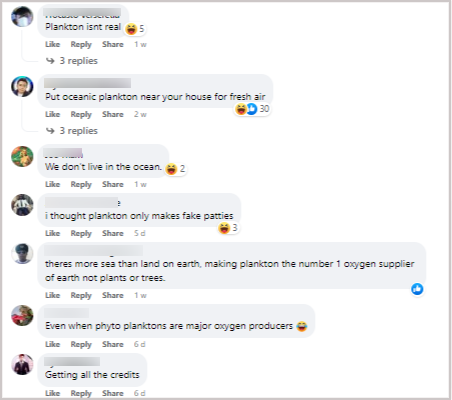
Meanwhile, some social media posts show that sea plankton produces the most Oxygen on Earth.

What we Found…
We researched for the answers to the question on the debate of oxygen-producing plants. We relied on the latest and trustworthy findings and scientific findings on the issue. As science is a dynamic field, all those findings are subject to change with time.
The uses of trees are common and familiar to all. But how about the uses of ocean plankton? It`s not that familiar. So, it`s worth taking a look at what sea plankton is.
What is Sea Plankton?
Plankton is marine and freshwater organisms that exist in a drifting state because they are nonmotile or too small or weak to swim against the current. The term plankton is a collective name for all such organisms—including certain algae, bacteria, protozoans, crustaceans, mollusks, and coelenterates, as well as representatives from almost every other phylum of animals. Plankton can be categorized into two main groups, phytoplankton and zooplankton. Phytoplankton includes organisms that do photosynthesis and produce food, while zooplankton feeds on phytoplankton.
Here, we consider phytoplankton as they perform photosynthesis, absorbing Carbon Dioxide and water to release Oxygen into the atmosphere. So, it’s a little misleading if someone states that sea plankton produces more oxygen. Why? Only phytoplankton photosynthesis and releases oxygen, while zooplankton is not like that. Details about it can be read here. Archived.
How much Oxygen comes from Sea Plankton?
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the US is a reputed organization that contains marine-related information. According to their website, about half of the earth’s Oxygen comes from sea plankton.
And at present, roughly half of the photosynthesis takes place in oceans and another half on land. Yet how much of this Oxygen produced in the ocean contributes to the air we breathe?
The majority of Oxygen produced by phytoplankton is used in marine life. This is because most living cells, including that marine life, use this oxygen for cellular respiration.
Oxygen is also consumed to decompose the dead material that accumulates in the ocean. Accordingly, some parts of marine water bodies are called “dead zones, because of the significantly lower level of Oxygen present. For an aerobic (oxygen-dependent) living being, it`s challenging to live in such areas. “Dead Zones” are primarily generated due to the extreme demand for oxygen to decompose dead algal blooms.
A minimal amount of oxygen produced in oceans escapes into the atmosphere at a prolonged rate. As a result, the air we breathe comprises of slow accumulation of O2, and the current Oxygen levels have been stable for a long time.
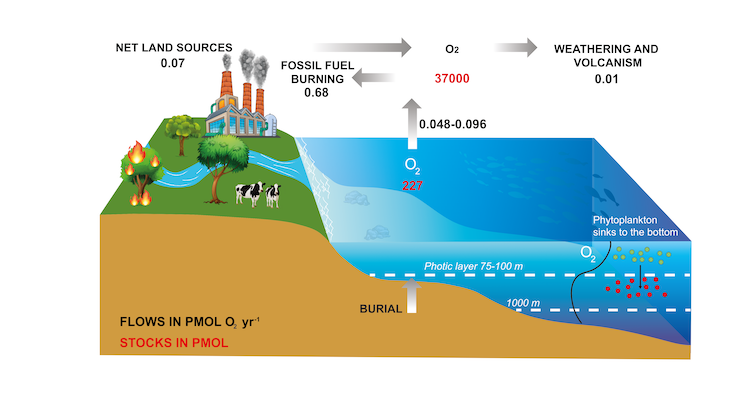
Furthermore, the exact percentage of oxygen released by phytoplankton is challenging to determine as it depends on various factors like the time of the day, tides, the year’s season, the nutritional lord of the seawater, etc., as seen here. Archived.
Role of Sea Plankton in Increasing Oxygen Percentage!
Currently, 78% of the Earth`s atmosphere consists of Nitrogen gas, while the Oxygen percentage is around 21%. However, the primitive atmosphere of the Earth had different concentrations of gases compared to the current composition.
From the beginning of the Earth till about 600 million years, the atmosphere included a mixture of Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen, while Oxygen remained at less than 5%.
So, who caused the increase in Oxygen concentration in the Earth`s atmosphere? It is mainly the microscopic ocean bacteria and plants (phytoplankton), with larger plants to a lesser extent.
Phytoplankton exists mainly on the top 200 meters from the ocean surface. To perform photosynthesis, sunlight is needed as the energy provider, and sun rays only penetrate about 200 meters deep into the water, leaving the remaining phytoplankton less efficient. More details about it can be read here. Archived.
Moreover, the lifespan of phytoplankton ranges from several days to a week, yet trees range from 50 – 5000 years. With time the efficiency of performing photosynthesis reduces. However, they are making phytoplankton look better at performing the same task. You can read more about this here. Archived.
Fighting climate change with bamboo
Oxygen Levels in Oceans and interlinked with Climate Change
The oceans span over 70% of the Earth’s surface and play a crucial role in acting up as a Carbon sink in absorbing a significant amount of CO2 present in the atmosphere. It is estimated that as much as one-quarter of the world’s annual carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are absorbed by oceans, mitigating climate change, and alleviating its impacts. More on this here
However, this also has come at a cost, with increased ocean acidification threatening coral and many delicate species. Moreover, the same oceans absorb a lot of heat reflected back to Earth due to global warming while leading to the oceanic temperature threatening the biodiversity of marine species and ecosystems.
Furthermore, this increase in sea temperatures leads to deoxygenation, meaning that warmer ocean water holds fewer oxygen levels. Another factor that inhibits oxygen generation in the oceans is the excessive growth of algae.
This means that the oxygen volume in the oceans has reduced by around 2% since the mid of last century and is expected to reduce further by the end of the current century due to global climate change and increased nutrient discharges.
Comments are closed.
Currently it looks like Expression Engine is the best blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Dear climatefactchecks.org administrator, You always provide clear explanations and step-by-step instructions.
Dear climatefactchecks.org admin, Thanks for the in-depth post!
Hello climatefactchecks.org webmaster, You always provide clear explanations and step-by-step instructions.