Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India

Climate change is the gradual shift in average weather conditions over time. The rapid climate change we are experiencing at present is mainly caused by human induced activities which have led to an increased rate of global warming. Hotter temperatures, melting glaciers, sea level rise and current flood and vast drought conditions are some of the results of rapid climate change. However, climate change is not only affecting humans, but animals too.
Freshwater fish are one such species who spend some or all of their lives in freshwater, such as rivers, ponds and lakes, with less than 1.05% saltiness level. Freshwater makes up only about 3 percent of the Earth’s water stock but nearly half of all fish species live in these freshwaters.
According to National Geographic, there are more than 10,000 freshwater fish species in the world, however, all of them are at some risk. Foremost and adverse effects of climate change on freshwater systems will likely be increased water temperatures, decreased dissolved oxygen levels, and the increased toxicity of pollutants.
Myth: Freshwater fish are less affected by global warming compared to the animals that live on land.
The habitats of freshwater fish species are threatened by global warming, mainly due to rising water temperatures. It is estimated that a 3.2 degree Celsius increase in global mean temperature would threaten more than half of the habitat for one third of all freshwater fish species. The number of species at risk is ten times smaller if warming is limited to 1.5 degrees. For more details, refer this article , archived.
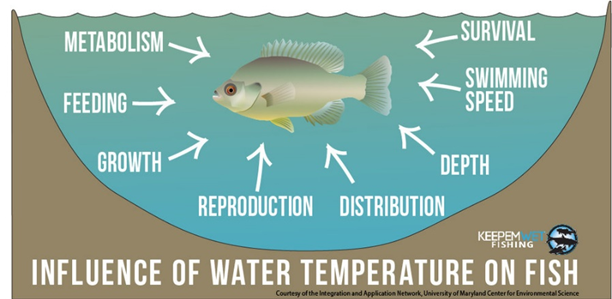
Increases in ground water temperature could also affect the quality of fish habitat. Fish have evolved to cope with specific hydrologic regimes and habitat niches. Fish communities may change with habitat niches. Therefore, changes of habitat conditions can cause a species to become extinct. Especially, endemic species, species in fragmented habitats will be less adept to follow changing thermal patterns over time. More can be read from here archived.
An increase in temperature is expected to produce changes in water circulation patterns, causing an increase in nutrient concentration in the hypolimnion (the deepest layer) and a decrease of productivity in the upper layer. These patterns could impact many species of freshwater fish, and the interactions between them, pushing the whole ecosystem into imbalance. More on this here Archived.
Myth: Impact of climate change on fish species is minimal, because fish can easily move around
If freshwater fish species would move freely across the water bodies and “escape” harmful conditions, theoretically they could minimize the hazardous conditions. However, many freshwater systems are fragmented, which impedes fish from moving to more suitable conditions.
River systems, lakes and other freshwater systems worldwide are threatened by man-made barriers like dams, weirs, sluices or culverts. These reduce the connectivity of freshwater habitats and limit opportunities for fish to respond to climate change by shifting their ranges. Even when fish could move, they have been threatened with anthropogenic activities.


Myth: Aquaculture is poisonous because of climate change
Aquaculture is the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of animals and plants in all types of water environments, including ponds, rivers, lakes, and the ocean. Global warming is leading to warmer water bodies in freshwater ecosystems and may result in increased occurrences of harmful algal blooms and pathogens. This is caused to be poisonous to aquacultures. More information here archived.
How Climate change effects fish growth

Fish growth is the comprehensive result of synergistic interactions between gene-determined growth potential and environmental conditions. Both are equally important for the success of growth. Increasing fish somatic cell growth rate were caused by the temperature variation directly, including water and air temperature induced by climate change.
In addition, climate change is expected to change the life history of benthos and planktons, which are the primary food source of fish and indirectly influence the energy intake and the growth of fish.
Fishing effects on global climate change
Dr.Parker said that, “Animal protein is an important source of nutrition but it is also one of the world’s largest contributors to global climate change, responsible for roughly half of all food production related emissions.” Fishing produces low CO2 emissions per unit output compared to other animal protein sources.
Another news passing through social media is that fishing has less impact on climate than the harvesting of other proteins. A study of greenhouse gas emissions of wild fisheries found that 1-5 Kg of carbon produce per 1kg of wild fish. More can be read from here Archived. However, emissions from fishing grew so fast in the past century. The ICES journal of marine science indicates that minor technological change in the fisheries industry has increased the contribution of climate change.
Conclusion:
Climate change affected so many variations on freshwater ecosystems. Changes of fish habitats as well as increased water temperatures, decreased dissolved oxygen levels, and the increased toxicity of pollutants predominantly affected fish growth, diversity of fish and species extinction. Anthropogenic activities also have reduced the ability of fish to overcome these conditions.