Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India

Climate change has become one of humanity’s most critical challenges in the 21st century. The scientific community, represented prominently by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), has provided compelling evidence that human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases, are the primary drivers of the observed global warming trend. However, despite this consensus, skepticism persists, and alternative theories have been proposed to explain the changing climate. This article delves into the various theories climate change skeptics put forth while presenting robust scientific evidence supporting the reality of human-induced climate change. By examining the different arguments skeptics raise, we aim to shed light on the scientific consensus and the urgent need for climate action.
Natural Fluctuations Theory
One of the prevailing arguments climate change skeptics put forth is that climate change is merely a natural phenomenon, and the Earth’s climate has always experienced fluctuations over time. This section examines the role of natural factors, such as solar variations and volcanic eruptions, in influencing historical climate changes. The Milankovitch Theory explains how three cyclical changes in Earth’s orbit and tilt lead to climate fluctuations occurring over tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of years. Glacial periods begin when these cycles align to increase winter solar radiation and reduce summer solar radiation at 65°N latitude. This creates conditions favoring higher temperatures and more water vapor, increasing snowfall. Cooler summers in the northern latitudes lead to less snow melting and glacier formation. The alignment of these orbital changes determines the amount of solar radiation received at different latitudes throughout the year, with the solar radiation reaching 65°N in the Northern Hemisphere playing a crucial role in the advance and retreat of glaciers and ice sheets. Link. Archived.
“Natural Fluctuations Theory” is not a term used in mainstream climate science. However, it refers to the argument made by some climate change skeptics that climate change is solely or predominantly driven by natural factors and variability rather than human activities.
While it is true that the Earth’s climate has experienced natural fluctuations throughout its history due to various factors such as solar variations, volcanic eruptions, and orbital changes (known as Milankovitch cycles), the scientific consensus is that the current rapid warming trend is primarily caused by human activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) and deforestation.
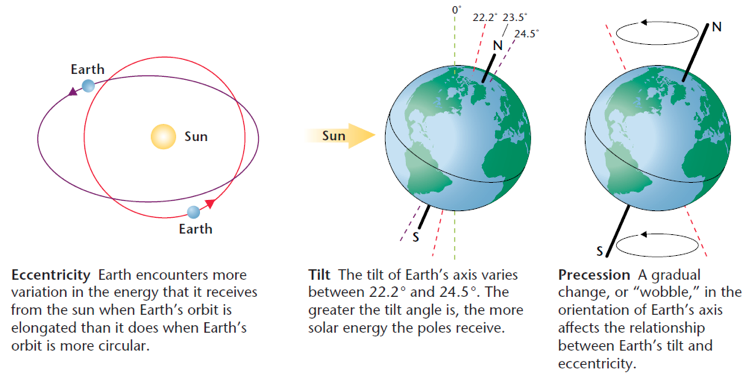
Image Source – Study Rocket
The Eruption Theory
Significant volcanic eruptions, particularly those with explosive force, have the potential to significantly impact Earth’s climate by releasing ash and sulfur dioxide gas. When these materials rise high into the stratosphere due to upper-level winds, they form a blanket that blocks sunlight from reaching the Earth’s surface. Instead, the sunlight is reflected into space, leading to a cooling effect and lowering the average temperature. One notable example is the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, which released enough sulfur dioxide to reduce global sunlight by 10% and cool the planet by 0.5°C for about a year. However, the largest eruption in human history was the 1815 eruption of Tambora in Indonesia, causing a “year without a summer” in 1816, leading to extreme cold temperatures worldwide and catastrophic harvest failures resulting in the loss of up to 200,000 lives in Europe. The effects of this massive eruption persisted for four to five years, with a 10% reduction in sunlight reaching Earth.
While natural factors can still influence short-term variations in climate, they cannot account for the significant and rapid rise in global temperatures observed over the past century. Human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases, have led to a substantial and unprecedented increase in global temperatures, causing widespread impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human societies.
Climate Change Conspiracy
Resistance to climate change action, often termed climate “skepticism” or “denialism,” varies in strength across regions but has become a potent political force worldwide, hindering binding efforts by domestic and global policymakers to address anthropogenic climate change. A significant portion of the population, exemplified by a 2013 poll in the United States showing nearly 40% of respondents, believes climate change to be a hoax. Climate skeptics challenge the widely accepted scientific consensus, attributing it to a manufactured or illusory agenda driven by various entities seeking to control society. This rhetoric reflects a rejection of scientific methods and undermines the role of science in shaping policy decisions. While some skeptics may genuinely dispute based on their interpretation of scientific evidence, surveys suggest that climate change denialism is often influenced by underlying conspiratorial thinking. This distrust of scientific findings and labeling such research as part of the conspiracy complicates efforts to address climate change and implement effective policies.
As we confront the multifaceted challenges of climate change, understanding people’s beliefs about this critical phenomenon becomes crucial. These beliefs span a spectrum, ranging from full awareness of climate change, its human-induced causes, and its adverse effects to various degrees of skepticism or outright denial. Researchers have proposed a framework that identifies three types of skepticism concerning global warming, later extended to investigate public beliefs about climate change as a whole. Trend skepticism questions the existence of climate change itself. Attribution skepticism doubts the role of human activities in causing climate change, with some attributing changes to human actions and others to natural environmental processes. Impact skepticism entails skepticism about the severity and detrimental effects of climate change. Studies, like the “Climate Change in the American Mind” surveys, have used this framework to explore public perceptions on the occurrence of global warming (trend dimension), its human causation (attribution dimension), and the perceived risks and harms it poses to individuals, society, and the environment (impact dimension). Such investigations provide valuable insights into how people conceptualize climate change.
Climate Change as a Hoax?
The idea of “Climate Change as a Hoax” is a conspiracy theory claiming climate change is not a real phenomenon and is deliberately fabricated or exaggerated by various entities for ulterior motives. This theory suggests that the scientific consensus on anthropogenic climate change, supported by overwhelming evidence and research, is somehow fraudulent or misleading. It is important to stress that the notion of climate change being a hoax is not supported by credible scientific evidence. The scientific community widely accepts the reality of climate change and its human-induced causes, primarily driven by greenhouse gas emissions from human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
Climate change has been extensively studied by climate scientists, environmental researchers, and international organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Their findings consistently point to the reality of climate change, its causes, and the urgency of taking action to mitigate its impacts. Conspiracy theories like the climate change hoax distract from the actual scientific evidence and undermine efforts to address climate change and implement effective policies. Climate change is a complex global challenge with far-reaching consequences for the environment, ecosystems, and human societies. Accepting the reality of climate change and working together to find sustainable solutions are critical steps in tackling this pressing issue.
In unraveling the theories and examining the scientific consensus, we must collectively acknowledge the reality of climate change and the imperative to act. Embracing science, seeking innovative solutions, and taking proactive steps toward a greener and more sustainable world will be instrumental in addressing climate change and safeguarding the well-being of future generations. The journey toward a sustainable future begins with a collective commitment to understanding, action, and environmental stewardship.
If you have any queries or come across suspicious content related to climate change or the environment and want us to verify them for you, then send them to us on our WhatsApp hotline: +917045366366
-With inputs from Dinesh Balasri–