Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India

Bees are considered as an essential part of biodiversity on the earth. Also, the existence of human life on Earth is believed to depend on the presence of bees.
Recently, posts have been shared on Twitter and other social media to sign petitions and collect donations to save bees. In those tweets, they mentioned that environmental degradation, encouraged by encroaching climate change, threatens endangered bee species as other insect pollinators.

International Bee Day 2023 was held on 20th May, highlighting the theme “Bee engaged in pollinator-friendly agriculture production.” With this, this year’s Bee’s Day celebration targeted global actions for pollinator-friendly agriculture productions, protecting bees and other pollinators from engaging and raising awareness of the importance of bees.
Bees Around the World
Bees are insect species that evolved from ancient predatory wasps 120 million years ago.
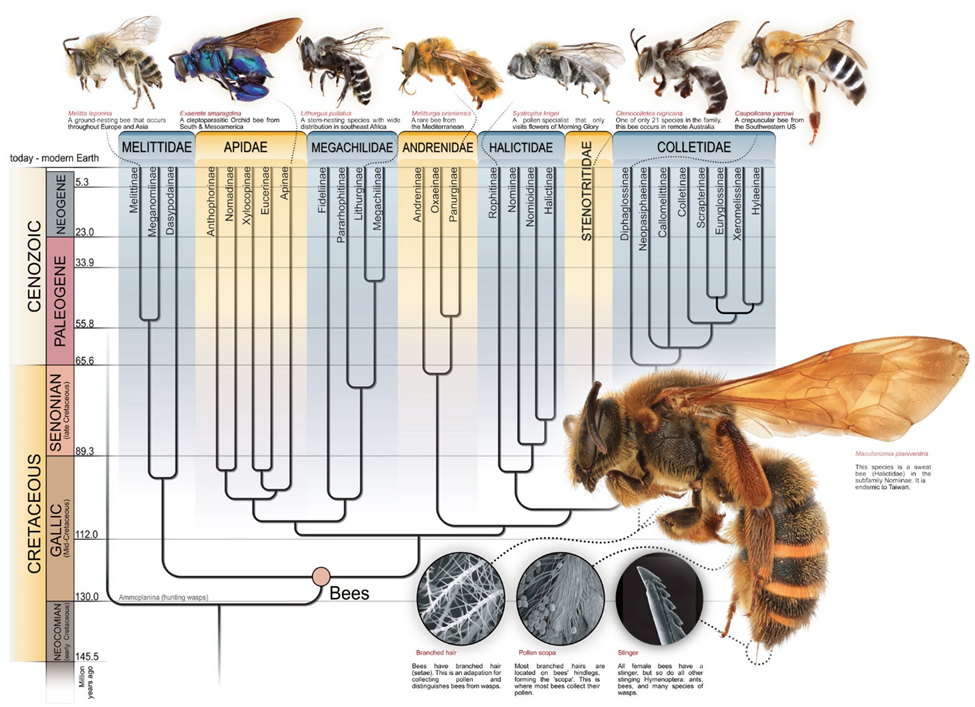
There are at least 2 trillion bees belonging to over 20,000 bee species that have been recognised worldwide. Bees can be found on every continent except Antarctica because of the need for plants and trees. According to the global map of bee distribution, bee diversity is higher in the Northern Hemisphere than Southern Hemisphere. Also, bees prefer to live in temperate regions over tropical regions. So, the bee diversity is higher in temperate regions than in the tropics. Northern America, Southern America, Southern Europe, Anatolia, Iran, East Asia and Southern Africa are the regions with higher bee diversity.
The most common bee species in the world is the Western honey bee (Apis mellifera). Other than that, there are many known, common bee species such as Bumblebee, Killer bee, Mining bee, Carpenter bee, Sweat bee, Megachile and more.
Because of the honey production of bees, to easily procure bee honey, people farm bees. China has the highest number of bee farms, and China is the world’s largest honey supplier.
Bees are social animals and live in colonies. A colony community builds a beehive, collects honey, and reproduces.
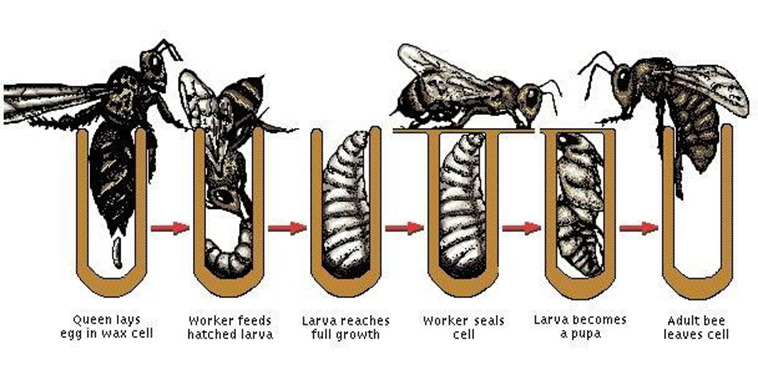
In a bee colony, there are three types of bees. They are workers, drones and the queen. Bee workers are female bees who can’t breed. Their duty during their lifetime is to do all the work in the hive. Their responsibilities include housekeeping, feeding the queen, larvae and drones, collecting pollen and nectar, and making wax.
Queen is the only female bee in the hive that can reproduce. Its genetic structure is similar to the workers’ but has a fully developed ovary. Throughout her life, the queen must lay lots of eggs and produce chemical scents that help regulate the colony’s unity.
Drone bees are the male bee type in a beehive. They must mate with the queen. These types of bees do not have stingers. They do not collect pollen or nectar and spend the whole day inside the hive. But when it comes to the seasons, which have fewer food sources to feed, worker bees chase the drones away from the beehive, leading to their death.
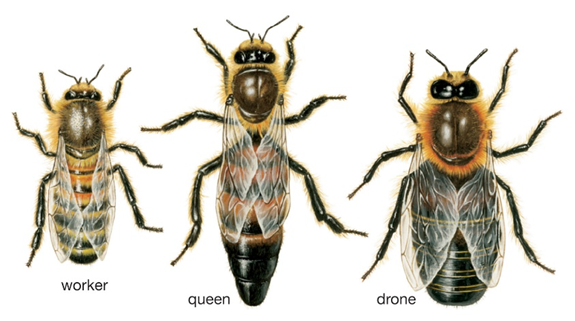
The lifespan of a bee can be varied according to its species and type. Typically, queen bees have the highest lifespan in a beehive. The average lifespan of a honey bee is eight months to 5 years.
Importance of Bees
Bees play an essential role in nature. As Albert Einstein said, the world depends on bees and their activities. This concept is well defined in the box office movie ‘Bee Movie’, 2007.

Pollination is an essential process in a plant for its reproduction. In pollination, pollen grains from the male anther of a flower are transferred to a female flower’s stigma. Anything that helps carry pollen towards the female flower’s stigma is called a pollinator. After pollinating, ovules in the female flower improve into a seed. This procedure continues the life cycle of plants and supports the ecosystem balance. To maintain life on earth, pollination has a significant duty.

Bees are the most excellent pollinator on the earth. Pollination contributes 30% of global food production. Bee-pollinated crops contribute around one-third of the total human dietary supply. Honey bees pollinate 80% of flowering plants, including more than 130 types of plants, fruits, and vegetables. Entire almond production is directly dependent on the pollination of honey bees. So, if there are no more bees, almonds won’t be there as well. Though the other crops do not rely 100% on bees, a higher percentage depends on bees and their pollination process. Other than almonds, apples, apricot, avocado, cranberry, melon, broccoli and many other fruits and vegetables. A high amount of the world’s food supply relies on bees.
Bees not only help pollinate food crops but other industrial crops as well. Some crops used for medicinal, industrial, fabric and other aspects are also pollinating and supported by bees. For example, the pollination of bees on willow and aspen trees is essential for producing over-the-counter drugs like aspirin. Opium poppies are used to make morphine.
Beeswax is another use from bees. Beeswax is used in cosmetic products as a thickening, emulsifying and stiffening agent. Also, beeswax is used as a medicine, which can be used in lowering cholesterol and relieving pain. Medicinal productions related to liver protection, acne treatment, stretch mark eliminator, and relaxer use beeswax as an ingredient.
Bee honey also is commonly used as a food source due to its higher nutrient value. Bee honey has medicinal value, being used as an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antibacterial agent.
Challenges to Bees
Though bees are a critical animal on the earth, they still have challenges like other animal species. Climate change is the main challenge bees are now facing.
Habitat loss is one of them. Bees select locations for their hives, considering many facts. They choose large hollows or cavities and view the flowers and plants near the area. When these habitats are destroyed, it is hard for bees to build a hive or produce honey.
Also, the decreasing of nectar sources is a challenge to bees. So, habitat protection is critical in protecting bees.
Pathogens, parasites infection and other diseases are other impairments to bees. For example, tropilaelaps mite, a parasite which parasitises Giant honey bees in Asia and European honey bees. This parasite causes severe damage to honey bee colonies. Zombie fungus also affects bees and their health. These infections and diseases can destroy whole colonies by initially affecting one individual.
Pesticides are commonly used in farming to control the insect pests that negatively affect the crops. But, some of these pesticides won’t stop from affecting only crops harming pest insects. They can be harmful to other insects in the farming area as well. So, bees also have to partake in the side effects of pesticides.
Predators who prey on bees are also a challenge to bees.

Air pollution is also a threat to bees. Bees are susceptible animals to air pollution. Recent studies have proved that air pollution can harm invertebrates, including bees’ ability to recognise Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from plants and flowers. This disrupts the bees’ and other invertebrate pollinators’ ability to seek food and nectar sources. Air pollution minimises the pollination of the plants in the area with polluted air.
Also, air pollution changes the bees’ food quality and abundance. The larval development of bees is being interfered with by air pollution.
But the main threat to the bee population is Climate Change.
Climate Changes on Bees
Climate change has been the main threat to the bee population and their existence.
Climate changes make differences in the environment and cause habitat loss for bees. Extreme dry weather and global warming due to climate changes harm bees’ habitats and destroy the flowers and other nectar sources. Also, extreme rainfall disturbs the flowering patterns of the plants. Heavy rain disrupts bees’ foraging patterns.
Changes in the seasons make destructive impacts on bees. Changes in seasons due to climate change affect bees’ foraging periods. When the foraging time is deducted, it reduces bees’ work efficiency. Changes in seasons shift the flowering period of plants and change the biological clock, which is a matter for foraging bees and their well-being.
Global warming increases the temperature in the environment and negatively impacts the bee’s body. With environment temperature, the body temperature of the bees also increases. This influences their flight activity speed. Cold temperatures in the environment have the same impact on bees. So, a frigid climate and too hot temperatures in the background can negatively impact bees’ activities and decrease their efficiency.
Climate change can increase the spreading of pathogens in bees. For example, the Varroa pathogen spreading speed among bees grows with climate change. Higher temperatures rise Varroa mite spreading.

Majorly, large bee species such as bumblebees are considered more vulnerable to global warming due to their lower heat tolerance. Compared to giant-sized bees, smaller bees have more patience in higher temperatures. According to the research, comb-building cavity nester bees also have less tolerance to climate change than soil-nesting bees.
Endangered Bee Species
From the Endangered Species Act of 1973, few bee species out of over 20,000 worldwide are listed as endangered bee species—the bee considered the most endangered species is the Rusty Patched Bumblebee (Bombus affinis).

Rusty Patterned Bumblebee, American Bumblebee, Franklin’s Bumblebee, Golden Northern Bumble Bee, Bombus occidentalis, Bombus fraternus and a few other bee species are on the endangered bee species list. According to that list of endangered bee species, it is clear that many of the endangered bee species belong to larger bee groups like bumblebees.
Climate changes, global warming, unexpected precipitation, early winter, late frost and drought are significant reasons for threatening the bee species. Apart from climate changes, pesticide and air pollution is the reason for threatening bee species.
How to Protect Bees?
“If the bee disappears from the earth’s surface, man would have no more than four years to live.”
Any step taken for bee protection is an excellent step leading to a safe future for the world and human survival.
Government policies and regulations should control human activities which impact negatively on bees. For example, one prominent human-causing harm to bees is using pesticides on crops. This action should be maintained if bees should be saved from the effect of them. Or the pesticides which are not harmful to bees and other pollinators should be discovered. Farmers should practise using more eco-friendly solutions to control crop-harming pests. There are alternatives to pesticides under cultural, biological, mechanical and natural pest control methods.
Air pollution reduction practices should be followed.
Climate change mitigation is also a topic that should be more attentive when discussing bee protection. To reduce the harms of bees by climate changes and protect them from driving towards extinction. Climate change mitigation can play a massive part in bee protection because many reasons that threaten bees originate from climate change.
Conclusion
Bees are one of the most important animals on the earth. And the existence of bees is essential to living on the planet, especially for humans. But bees are now threatened because of climate change and other reasons. Some species are already listed under the endangered category. Doing everything to save the bees and develop the bee population in the world is not only a remarkable service to nature but also to ourselves as well.
-With inputs from Mihiri Saparamadhu–