Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India
Physical Address
23,24,25 & 26, 2nd Floor, Software Technology Park India, Opp: Garware Stadium,MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad, Maharashtra – 431001 India

Studies confirm that trace gas Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is one of the major Greenhouse Gases (GHG) causing global warming and significantly contributes to global climate change. Henceforth, many efforts have been made worldwide to limit human-induced Carbon Dioxide gas emissions and towards novel carbon capture techniques.
However, many climate change deniers downplay the CO2 emission levels and their impacts on climate change. As a result, every time there is a major volcanic eruption, social media posts often go viral, claiming that the amount of CO2 emitted by such volcanic eruptions stands at a much larger level as compared to emissions caused by humans.
Let’s look at these claims first.
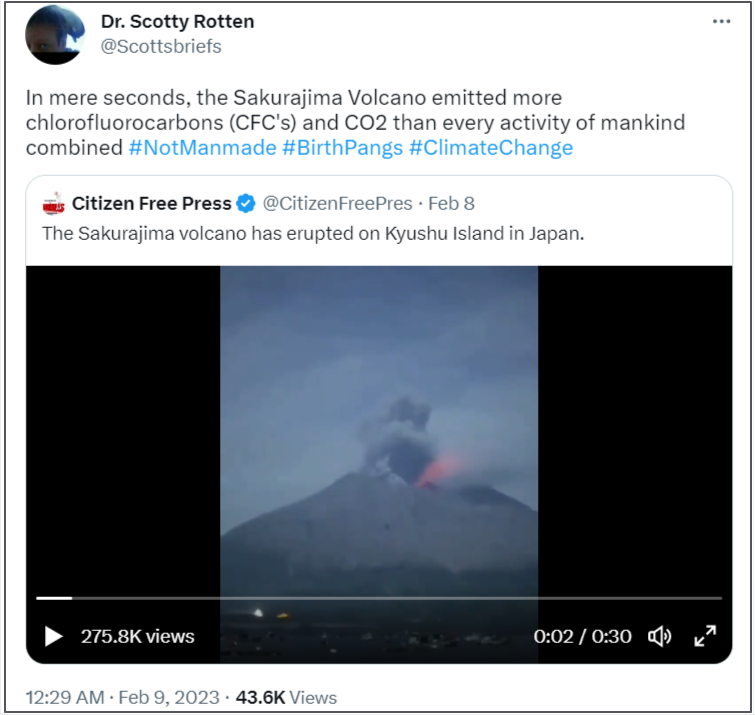
In early February, the Sakurajima volcano erupted in southwestern Japan. Soon after, a Tweet claimed, “In mere seconds, the Sakurajima Volcano emitted more chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and CO2 than every activity of mankind combined #NotManmade #BirthPangs #ClimateChange.” as seen below.
Similarly, when one of the most active volcanoes in Indonesia, Mt Merapi, erupted on the 11th of March, one Facebook user stated that the amount of Carbon Dioxide released into the atmosphere as a result of this eruption was more than the CO2 levels released by human activities since the Industrial Revolution!

Mount Etna in Italy is one of the world’s most active volcanoes and similar claims get shared every time a major eruption occurs around this volcano. In 2022, when such an eruption occurred, a viral Tweet claimed that the burst released 10,000 times the CO2 into the atmosphere than the amount entire humanity has contributed during their time on Earth. The Tweet, which had been addressed to all environmentalists, can be viewed here. Archived
But are the CO2 emission levels related to volcanos such concerning?
Volcanic eruptions do indeed release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. However, the posts exaggerate the CO2 emissions levels by many folds and are helping instigate misconceptions about global warming. It is dangerous as it could motivate people to emit more carbon dioxide and continue to turn a blind eye toward GHG emissions, which would accelerate climate change.
To take things into perspective, researchers estimate that around 50 million tons of CO2 were released into the atmosphere during the Mt. Pinatubo (Philippines) eruption in 1991, one of the major volcanic eruptions in the 20th century. However, human-induced CO2 emission during a single day is closer to twice that amount. More details can be read here |Archived
Mount St. Helens, in the USA, and Mount Pinatubo, in the Philippines, were the most significant volcanic eruptions during the last century. During such enormous eruptions, a large amount of CO2 is released into the atmosphere in a few hours, which can be on par with emissions caused by human activities during the same time. However, human emissions continue to happen daily and year after year, whereas enormous volcanic eruptions are very rare.
According to NASA, “Human activities emit a Mount St. Helens-sized eruption of CO2 every 2.5 hours and a Mount Pinatubo-sized eruption of CO2 twice daily.” It further says human contributions to the carbon cycle are more than 100 times those from all the volcanoes in the world – combined. The NASA article can be read here | Archived.
Volcanoes and volcanic regions alone outgas an estimated 280-360 million tones (0.28 to 0.36 Gt) of CO2 per year, according to the ten years long Deep Carbon Observatory Program by the National Academy of Sciences, Washington. The details about the research can be read here. Archived.
According to a report by International Energy Authority (IEA), the global energy-related anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide gas release of the year 2021 itself was around 36.3 billion tones (36 Gt). The report about it can be read here | Archived. The 2022 IEA report shows a further increase in (CO2) emissions from energy combustion and industrial processes with 36.8 Gt.
Therefore, considering that all the volcanoes combined emit only around 0.36 Gt of Carbon Dioxide annually, CO2 emissions by anthropogenic activities during a year are 100 times more than that of volcanic activities combined.
Even though there has been a slight increase in the number of eruptions, taking the number of active eruptions and their intensities in the past several decades, it is noticed that there isn’t a significant increase in impact in volcano activities across the planet.
However, the amount of atmospheric CO2 (ppm) has sharply risen during the last few centuries, ever since the industrial revolution, as seen here. During the past several decades, CO2 levels have kept on increasing at an alarming rate.
Since volcanic activities have mostly remained stable during the past few decades, it’s clear that these eruptions are not a main contributor to the increased CO2 levels. On the contrary, anthropogenic activities are responsible for much of this increase in CO2 levels.
As per the USGS (United States Geological Survey), “Volcanoes are openings, or vents where lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions can last days, months, or even years.” Volcanos can appear in different forms, including undersea eruptions.
According to the USGS, molten rock from Earth’s superheated mantle continuously rises from deep under Earth’s crust. It forms new ocean floors along oceanic ridges where tectonic plates push past one another beneath deep water. Theoretically, every location along the ridge where molten lava is meeting ocean water is a volcano. Other than those locations, there are only roughly 500 historically known eruptions from the world’s 1,350 potentially active volcanoes. While being largely transient, they have had significant effects on the climate.
So, yes. Volcanoes can impact the global climate. Huge quantities of volcanic gas, aerosol droplets, and ash are injected into the stratosphere during massive explosive eruptions. The majority of the injected ash gets cleared from the stratosphere within a few days to weeks and has no effect on climate change. But volcanic carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, has the ability to support global warming; volcanic gases like sulfur dioxide can actually cause global cooling.
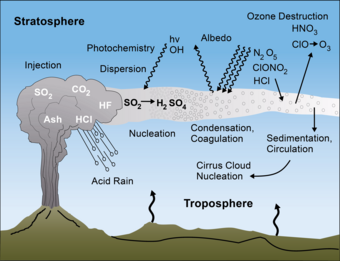
Aside from its potential to form global cooling and acid rains, volcanic HCl presents another danger as it threatens Earth’s ozone layer. HCl breaks down quickly into chlorine (Cl) and chlorine monoxide (ClO). Chlorine destroys ozone. In fact, during volcanic eruptions in Chile and the Philippines, satellite data revealed an up to 20% depletion of ozone around the massive Mt. Pinatubo volcanic eruptions in 1991.
In a more recent example, Hunga Tonga’s undersea volcanic eruption shook the world in early 2022, and scientists believe that an enormous amount of water vapor was injected into the stratosphere, which has the potential to make the ozone hole larger in the coming years.
If you have any queries or come across suspicious content related to climate change or the environment and want us to verify them for you, do share them with us on Climate Buddy, our WhatsApp tipline number: +917045366366
According to our investigation, it`s clear that Carbon Dioxide emissions as a result of human-induced industrial activities contribute significantly more towards the world`s total Carbon Dioxide levels as compared to the CO2 emissions during a volcanic eruption.
-With Inputs from Nuwandhara Mudalige –